
前言
本手册(当前 V1 Beta)大概 3 万 7 千字,由于篇幅限制,这里仅罗列手册中的关键目录结构,也算是一种导读。完整内容可见:
https://github.com/slowmist/Blockchain-dark-forest-selfguard-handbook
我们选择 GitHub 平台作为本手册的首要发布位置是因为:方便协同及看到历史更新记录。你可以 Watch、Fork 及 Star,当然我们更希望你能参与贡献。
好,导读开始...
如果你持有加密货币或对这个世界有兴趣,未来可能会持有加密货币,那么这本手册值得你反复阅读并谨慎实践。本手册的阅读需要一定的知识背景,希望初学者不必恐惧这些知识壁垒,因为其中大量是可以“玩”出来的。
在区块链黑暗森林世界里,首先牢记下面这两大安全法则:
零信任:简单来说就是保持怀疑,而且是始终保持怀疑。
持续验证:你要相信,你就必须有能力去验证你怀疑的点,并把这种能力养成习惯。
关键内容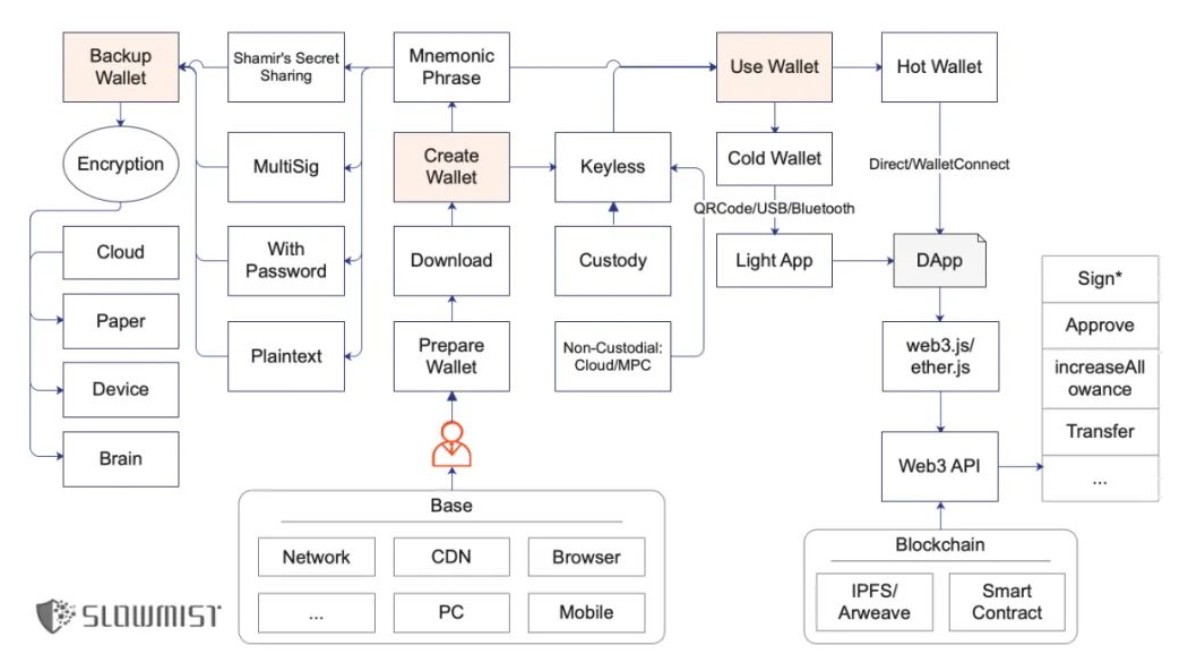
一、创建钱包
- Download
1. 找到正确的官网
a. Google
b. 行业知名收录,如 CoinMarketCap
c. 多问一些比较信任的人
2. 下载安装应用
a. PC 钱包:建议做下是否篡改的校验工作(文件一致性校验)
b. 浏览器扩展钱包:注意目标扩展下载页面里的用户数及评分情况
c. 移动端钱包:判断方式类似扩展钱包
d. 硬件钱包:从官网源头的引导下购买,留意是否存在被异动手脚的情况
e. 网页钱包:不建议使用这种在线的钱包
- Mnemonic Phrase
创建钱包时,助记词的出现是非常敏感的,请留意你身边没有人、摄像头等一切可以导致偷窥发生的情况。同时留意下助记词是不是足够随机出现
- Keyless
1. Keyless 两大场景(此处区分是为了方便讲解)
a. Custody,即托管方式。比如中心化交易所、钱包,用户只需注册账号,并不拥有私钥,安全完全依托于这些中心化平台
b. Non-Custodial,即非托管方式。用户唯一掌握类似私钥的权力,但却不是直接的加密货币私钥(或助记词)
2. MPC 为主的 Keyless 方案的优缺点
二、备份钱包
- 助记词/私钥类型
1. 明文:12 个英文单词为主
2. 带密码:助记词带上密码后会得到不一样的种子,这个种子就是之后拿来派生出一系列私钥、公钥及对应地址
3. 多签:可以理解为目标资金需要多个人签名授权才可以使用,多签很灵活,可以设置审批策略
4. Shamir's Secret Sharing:Shamir 秘密共享方案,作用就是将种子分割为多个分片,恢复钱包时,需要使用指定数量的分片才能恢复
- Encryption
1. 多处备份
a. Cloud:Google/Apple/微软,结合 GPG/1Password 等
b. Paper:将助记词(明文、SSS 等形式的)抄写在纸卡片上
c. Device:电脑/iPad/iPhone/移动硬盘/U 盘等
d. Brain:注意脑记风险(记忆/意外)
2. 加密
a. 一定要做到定期不定期地验证
b. 采用部分验证也可以
c. 注意验证过程的机密性及安全性
三、使用钱包
- AML
1. 链上冻结
2. 选择口碑好的平台、个人等作为你的交易对手
- Cold Wallet
1. 冷钱包使用方法
a. 接收加密货币:配合观察钱包,如 imToken、Trust Wallet 等
b. 发送加密货币:QRCode/USB/Bluetooth
2. 冷钱包风险点
a. 所见即所签这种用户交互安全机制缺失
b. 用户的有关知识背景缺失
- Hot Wallet
1. 与 DApp(DeFi、NFT、GameFi 等)交互
2. 恶意代码或后门作恶方式
a. 钱包运行时,恶意代码将相关助记词直接打包上传到黑客控制的服务端里
b. 钱包运行时,当用户发起转账,在钱包后台偷偷替换目标地址及金额等信息,此时用户很难察觉
c. 破坏助记词生成有关的随机数熵值,让这些助记词比较容易被破解
- DeFi 安全到底是什么
1. 智能合约安全
a. 权限过大:增加时间锁(Timelock)/将 admin 多签等
b. 逐步学会阅读安全审计报告
2. 区块链基础安全:共识账本安全/虚拟机安全等
3. 前端安全
a. 内部作恶:前端页面里的目标智能合约地址被替换/植入授权钓鱼脚本
b. 第三方作恶:供应链作恶/前端页面引入的第三方远程 JavaScript 文件作恶或被黑
4. 通信安全
a. HTTPS 安全
b. 举例:MyEtherWallet 安全事件
c. 安全解决方案:HSTS
5. 人性安全:如项目方内部作恶
6. 金融安全:币价、年化收益等
7. 合规安全
a. AML/KYC/制裁地区限制/证券风险有关的内容等
b. AOPP
- NFT 安全
1. Metadata 安全
2. 签名安全
- 小心签名/反常识签名
1. 所见即所签
2. OpenSea 数起知名 NFT 被盗事件
a. 用户在 OpenSea 授权了 NFT(挂单)
b. 黑客钓鱼拿到用户的相关签名
3. 取消授权(approve)
a. Token Approvals
b. Revoke.cash
c. APPROVED.zone
d. Rabby 扩展钱包
4. 反常识真实案例
- 一些高级攻击方式
1. 针对性钓鱼
2. 广撒网钓鱼
3. 结合 XSS、CSRF、Reverse Proxy 等技巧(如 Cloudflare 中间人攻击)
四、传统隐私保护
- 操作系统
1. 重视系统安全更新,有安全更新就立即行动
2. 不乱下程序
3. 设置好磁盘加密保护
- 手机
1. 重视系统的安全更新及下载
2. 不要越狱、Root 破解,除非你玩安全研究,否则没必要
3. 不要从非官方市场下载 App
4. 官方的云同步使用的前提:账号安全方面你确信没问题
- 网络
1. 网络方面,尽量选择安全的,比如不乱连陌生 Wi-Fi
2. 选择口碑好的路由器、运营商,切勿贪图小便宜,并祈祷路由器、运营商层面不会有高级作恶行为出现
- 浏览器
1. 及时更新
2. 扩展如无必要就不安装
3. 浏览器可以多个共存
4. 使用隐私保护的知名扩展
- 密码管理器
1. 别忘记你的主密码
2. 确保你的邮箱安全
3. 1Password/Bitwarden 等
- 双因素认证
Google Authenticator/Microsoft Authenticator 等
- 科学上网
科学上网、安全上网
- 邮箱
1. 安全且知名:Gmail/Outlook/QQ 邮箱等
2. 隐私性:ProtonMail/Tutanota
- SIM 卡
1. SIM 卡攻击
2. 防御建议
a. 启用知名的 2FA 工具
b. 设置 PIN 码
- GPG
1. 区分
a. PGP 是 Pretty Good Privacy 的缩写,是商用加密软件,发布 30 多年了,现在在赛门铁克麾下
b. OpenPGP 是一种加密标准,衍生自 PGP
c. GPG,全称 GnuPG,基于 OpenPGP 标准的开源加密软件
- 隔离环境
1. 具备零信任安全法则思维
2. 良好的隔离习惯
3. 隐私不是拿来保护的,隐私是拿来控制的
五、人性安全
- Telegram
- Discord
- 来自“官方”的钓鱼
- Web3 隐私问题
六、区块链作恶方式
- 盗币、恶意挖矿、勒索病毒、暗网交易、木马的 C2 中转、洗钱、资金盘、博彩等
- SlowMist Hacked 区块链被黑档案库
七、被盗了怎么办
- 止损第一
- 保护好现场
- 分析原因
- 追踪溯源
- 结案
八、误区
- Code Is Law
- Not Your Keys, Not Your Coins
- In Blockchain We Trust
- 密码学安全就是安全
- 被黑很丢人
- 立即更新
总结
当你阅读完本手册后,一定需要实践起来、熟练起来、举一反三。如果之后你有自己的发现或经验,希望你也能贡献出来。如果你觉得敏感,可以适当脱敏,匿名也行。其次,致谢安全与隐私有关的立法与执法在全球范围内的成熟;各代当之无愧的密码学家、工程师、正义黑客及一切参与创造让这个世界更好的人们的努力,其中一位是中本聪。最后,感谢贡献者们,这个列表会持续更新,有任何的想法,希望你联系我们。
导读到此,完整版本,欢迎阅读并分享 :)
https://github.com/slowmist/Blockchain-dark-forest-selfguard-handbook
Produced by SlowMist | Cosine: Blockchain Dark Forest Self-Help Manual Preface Blockchain is a great invention, which has brought about changes in some production relations, allowing the precious thing of "trust" to be partially solved. However, the reality is cruel, and there are many misunderstandings in people's understanding of the blockchain. These misunderstandings have led to the bad guys easily taking advantage of the loopholes and frequently putting their black hands into people's wallets, causing a lot of financial losses. This is already a dark forest.
Based on this, Cosine, the founder of SlowMist Technology, outputs the self-help manual in the dark forest of blockchain.
This manual (current V1 Beta) is about 37,000 words. Due to space limitations, only the key directory structure in the manual is listed here, which can also be regarded as a guide. The complete content can be found at: https://github.com/slowmist/Blockchain-dark-forest-selfguard-handbook We chose the GitHub platform as the primary publishing location for this manual because it is convenient for collaboration and viewing historical update records. You can Watch, Fork and Star, of course we hope you can contribute.
Well, the introduction begins... Introduction If you hold cryptocurrencies or are interested in the world, you may hold cryptocurrencies in the future, then this manual is worth your repeated reading and careful practice. The reading of this manual requires a certain background of knowledge. I hope beginners do not have to fear these knowledge barriers, because a lot of them can be "played".
In the dark forest world of the blockchain, first keep in mind the following two security laws: Zero Trust: Simply put, be suspicious, and always be suspicious.
Continuous Verification: If you want to believe, you must have the ability to verify your doubts and make this ability a habit.
Key content 1. Create a walletDownload1. Find the correct official website a. Google b. Well-known industry records, such as CoinMarketCap c. Ask more trusted people 2. Download and install the application a. PC wallet: It is recommended to check whether it has been tampered with work (document consistency check)
b. Browser extension wallet: Pay attention to the number of users and ratings on the download page of the target extension c. Mobile wallet: The judgment method is similar to the extension wallet d. Hardware wallet: Buy under the guidance of the official website source, and pay attention to whether there is any cheating Situation e. Web wallet: It is not recommended to use this kind of online wallet. When Mnemonic Phrase creates a wallet, the appearance of the mnemonic phrase is very sensitive. Please pay attention to the situation that there is no one around you, cameras, etc., which can lead to voyeurism. At the same time, pay attention to whether the mnemonic words are enough to randomly appear in the two scenarios of Keyless1. Keyless (the distinction here is for the convenience of explanation)
a. Custody, the custody method. For example, in centralized exchanges and wallets, users only need to register an account and do not own a private key. The security relies entirely on these centralized platforms. b. Non-custodial, that is, a non-custodial method. The only power that the user has a similar private key, but not the direct encrypted private key (or mnemonic)
2. The advantages and disadvantages of the MPC-based Keyless scheme 2. Backup wallet mnemonic/private key type 1. Plaintext: 12 English words are the main 2. With password: After the mnemonic is added with the password, a different seed will be obtained , this seed is then used to derive a series of private keys, public keys and corresponding addresses 3. Multi-signature: It can be understood that the target funds require multiple signatures and authorization before they can be used. Multi-signature is very flexible, and an approval strategy can be set. 4. Shamir's Secret Sharing: Shamir secret sharing scheme, the function is to divide the seed into multiple shards. When restoring the wallet, you need to use a specified number of shards to restore Encryption1. Multiple backups a. Cloud: Google/Apple/Microsoft, combined with GPG/ 1Password, etc. b. Paper: Copy the mnemonic (in plain text, SSS, etc.) on the paper card c. Device: Computer/iPad/iPhone/mobile hard disk/U disk, etc. d. Brain: Pay attention to the risks of brain memory (memory/ Accident)
2. Encryption a. It must be verified regularly and irregularly b. Partial verification is also possible c. Pay attention to the confidentiality and security of the verification process 3. Use wallet AML1. Freeze on the chain 2. Choose a platform with a good reputation, an individual Wait as your counterparty Cold Wallet1. How to use cold wallet a. Receive cryptocurrency: cooperate with observation wallet, such as imToken, Trust Wallet, etc. b. Send cryptocurrency: QRCode/USB/Bluetooth2. Cold wallet risk point a. What you see is what you see The signed user interaction security mechanism is missing b. The user's relevant knowledge background is missing Hot Wallet1. Interacting with DApps (DeFi, NFT, GameFi, etc.) 2. Malicious code or backdoor ways of doing evil a. When the wallet is running, malicious code will help The recorded words are directly packaged and uploaded to the server controlled by the hacker. b. When the wallet is running, when the user initiates a transfer and secretly replaces the target address and amount and other information in the wallet background, it is difficult for the user to notice at this time. c. The entropy value of random numbers makes these mnemonics easier to crack. What exactly is DeFi security 1. Smart contract security a. Excessive permissions: increase the timelock (Timelock) / multi-sign the admin, etc. b. Gradually learn to read the security audit report 2. Blockchain basic security: consensus ledger security/virtual machine security, etc. 3. Front-end security a. Internal evil: The target smart contract address in the front-end page is replaced/implanted with authorized phishing scripts b. Third-party evil: supply chain evil /The third-party remote JavaScript file introduced by the front-end page is malicious or hacked 4. Communication security a. HTTPS security b. Example: MyEtherWallet security incident c. Security solution: HSTS5. Currency price, annualized income, etc. 7. Compliance and security a. AML/KYC/sanctioned area restrictions/security risks, etc. b. AOPPNFT security 1. Metadata security 2. Signature security careful signature/anti-common sense signature 1. Seen 2. Several well-known NFT theft incidents in OpenSea a. The user authorized the NFT (pending order) in OpenSea
b. The hacker phishing to get the relevant signature of the user 3. Cancel authorization (approve)
a. Token Approvals b. Revoke.cash c. APPROVED.zone d. Rabby extended wallet Tricks (like Cloudflare man-in-the-middle attacks)
4. Traditional privacy protection operating systems 1. Pay attention to system security updates, and act immediately if there are security updates. 2. Don’t mess with the program. 3. Set up disk encryption to protect the phone. 1. Pay attention to system security updates and downloads. , unless you play security research, it is not necessary 3. Don't download App from unofficial markets Unfamiliar Wi-Fi2. Choose a router and operator with a good reputation, do not covet petty cheap, and pray that there will be no advanced malicious behavior at the router and operator level . Browsers can coexist 4. Use a well-known extended password manager for privacy protection Scientific Internet access, secure Internet access mailbox1. Safe and well-known: Gmail/Outlook/QQ mailbox, etc.2. Privacy: ProtonMail/TutanotaSIM card1. SIM card attack2. Defense suggestion a. Enable well-known 2FA tools b. Set PIN code GPG1 . Differences a. PGP is the abbreviation of Pretty Good Privacy, which is a commercial encryption software, released for more than 30 years, and now under the command of Symantec b. OpenPGP is an encryption standard, derived from PGP c. GPG, full name GnuPG, based on OpenPGP Standard Open Source Encryption Software Isolation Environment 1. Have Zero Trust Security Law Thinking 2. Good Isolation Habits 3. Privacy is not for protection, privacy is for control 6. Ways to do evil in the blockchain: Stealing coins, malicious mining, ransomware, dark web transactions, C2 transfer of Trojans, money laundering, fund disks, gambling, etc. SlowMist Hacked blockchain is hacked archives 7. What should I do if it is stolen? Loss first, protect the scene, analyze the cause, trace the source, and close the case 8. Misunderstanding Code Is Law , Become proficient, infer other things. If you have your own discoveries or experiences in the future, I hope you can contribute as well. If you feel sensitive, you can desensitize appropriately, or anonymously. Second, thanks to the global maturity of security and privacy-related legislation and enforcement; the efforts of all generations of well-deserved cryptographers, engineers, righteous hackers, and everyone involved in creating a better world, one of whom is Nakamoto Cong. Finally, thanks to the contributors, this list will be continuously updated, if you have any ideas, I hope you will contact us.
Guide to this, the full version, welcome to read and share :)
https://github.com/slowmist/Blockchain-dark-forest-selfguard-handbook
