2022.09.21 本文发布
2023.03.02 更新官方最新表格10.6 10.11
2024.06.07 更新官方最新表格 11.5
MySQL5.6 5.7 8.0 产品生命周期及分支MariaDB 生命周期停止服务更新时间 独家大全摘自官方
经常会被问到MySQL各个版本的生命周期,以及如何选择MySQL版本的问题。今天在这里主要向各位介绍一下MySQL产品的生命周期。
MySQL被Oracle收购之后,在产品的开发上面变得比之前更加规范,并且参照了Oracle其它产品的开发模式,产品会遵循事先制定的生命周期去开发维护。事先制定好的生命周期,对于用户来说是非常有利的事情,用户可以参照数据库产品的生命周期,根据项目情况,选择适合自己的产品版本。
官方最新表格
MariaDB general release maintenance periods
Rolling release
| Release | Stable (GA) Date |
|---|---|
| 11.5 | In development |
Currently maintained long-term releases
Currently maintained short-term releases
Unmaintained releases
| Release series | Stable (GA) Date | End-of-life |
|---|---|---|
| 11.3 | 16 Feb 2024 | Rolling |
| 10.10 | 17 Nov 2022 | 17 Nov 2023 |
| 10.9 | 22 Aug 2022 | 22 Aug 2023 |
| 10.8 | 20 May 2022 | 20 May 2023 |
| 10.7 | 9 Feb 2022 | 9 Feb 2023 |
| 10.3 | 25 May 2018 | 25 May 2023 |
| 10.2 | 23 May 2017 | 23 May 2022 |
| 10.1 | 17 Oct 2015 | 17 Oct 2020 |
| 10.0 | 31 Mar 2014 | 31 Mar 2019 |
| 5.5 | 11 Apr 2012 | 11 Apr 2020 |
| 5.3 | 29 Feb 2012 | 1 Mar 2017 |
| 5.2 | 10 Nov 2010 | 10 Nov 2015 |
| 5.1 | 1 Feb 2010 | 1 Feb 2015 |
These dates constitute the public policy of the MariaDB Foundation and are not legally binding. The software is released with the GPL license as-is, without warranties.
oracle MySQL版本和MariaDB版本对应表:
MariaDB版本 MySQL版本
MariaDB 10.3 发布时间2018 MySQL 8.0 发布时间2018
MariaDB 10.2 发布时间2017 MySQL 5.7 发布时间2015
MariaDB 10.1 发布时间2015 MySQL 5.6 发布时间2013
MariaDB 10.0 发布时间2014 MySQL 5.5 发布时间2010
MariaDB 5.5 发布时间2012 MySQL 5.1 发布时间2008
MySQL 5.0 发布时间2005
让我们先看一下MySQL产品的生命周期是怎样定义的。
https://www.mysql.com/cn/support/
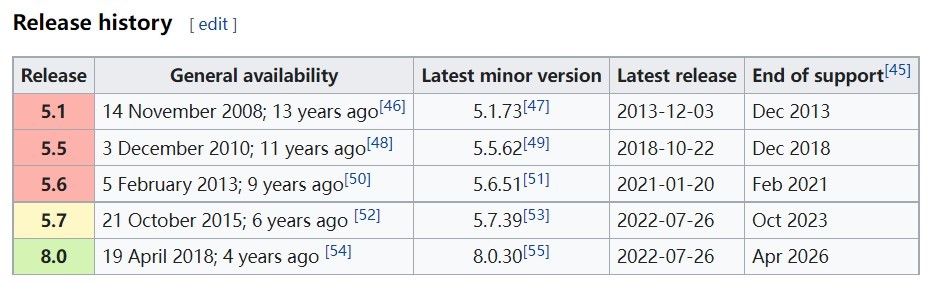
产品的生命周期分为三个支持阶段,标准支持服务、延伸支持服务和持续支持服务,对应这三个阶段的时间分别是产品从GA(正式发布)开始1-5年、6-8年及9年以上。对应不同阶段,所提供的服务已经显示在上面这个表里。乍一看标准支持和延伸支持服务没有区别,事实上区别还是有一些的,主要在于,进入延伸支持阶段后,产品不会像之前那样频繁的进行版本维护和发布补丁,原则上只会发布安全补丁。对于MySQL社区版的用户来说,非常关心社区版的MySQL是否和商业版的MySQL同样提供版本维护和补丁。这一点请大家可以放心,从Oracle接手MySQL到目前为止,社区版和商业版的补丁一直是同步发行的。
MariaDB是mysql完美替代者 相关文章推荐
推荐先看此文 MySQL与MariaDB性能比拼,哪个更出色?
MariaDB general release maintenance periods
| Major and Minor Version | Stable (GA) Date | End-of-life |
|---|---|---|
| 5.1 | 1 Feb 2010 | 1 Feb 2015 |
| 5.2 | 10 Nov 2010 | 10 Nov 2015 |
| 5.3 | 29 Feb 2012 | 1 Mar 2017 |
| 5.5 | 11 Apr 2012 | 11 Apr 2020 |
| 10.0 | 31 Mar 2014 | 31 Mar 2019 |
| 10.1 | 17 Oct 2015 | 17 Oct 2020 |
| 10.2 | 23 May 2017 | 23 May 2022 |
| 10.3 | 25 May 2018 | 25 May 2023 |
| 10.4 | 18 Jun 2019 | 18 Jun 2024 |
| 10.5 | 24 Jun 2020 | 24 Jun 2025 |
| 10.6 | 6 Jul 2021 | 6 Jul 2026 |
| 10.7 | 9 Feb 2022 | 9 Feb 2023 |
| 10.8 | 20 May 2022 | 20 May 2023 |
| 10.9 | 22 Aug 2022 | 22 Aug 2023 |
| 10.10 | TBC | TBC |
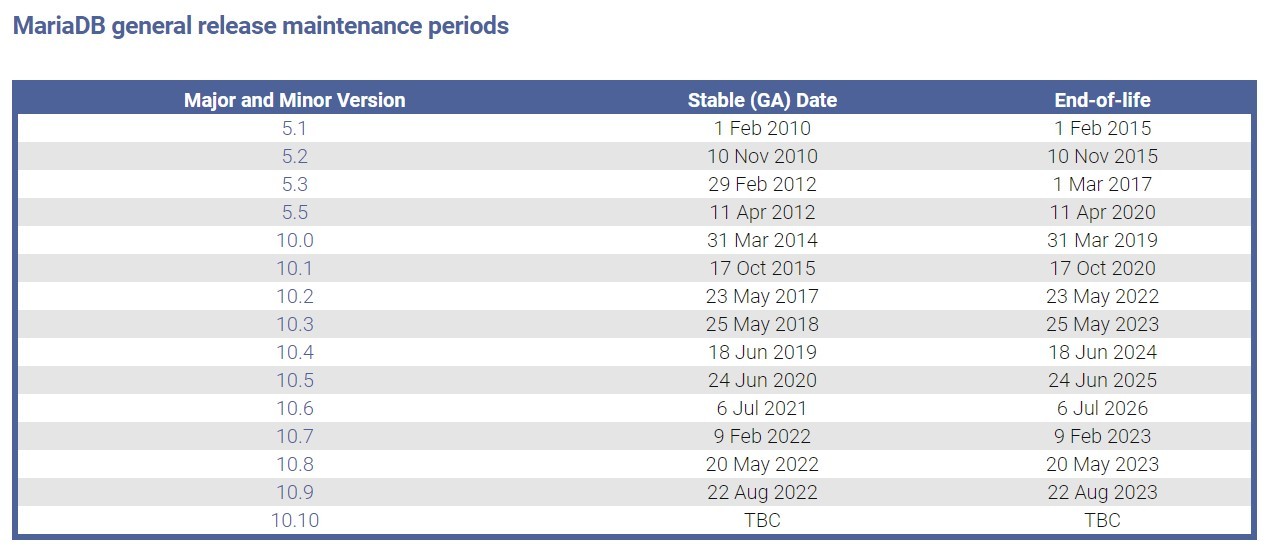
These dates constitute the public policy of the MariaDB Foundation and are not legally binding. The software is released with the GPL license as-is, without warranties.
Currently maintained long-term releases
| Release series | Stable (GA) Date | End-of-life |
|---|---|---|
| 10.3 | 25 May 2018 | 25 May 2023 |
| 10.4 | 18 Jun 2019 | 18 Jun 2024 |
| 10.5 | 24 Jun 2020 | 24 Jun 2025 |
| 10.6 | 6 Jul 2021 | 6 Jul 2026 |
| 10.11 | 16 Feb 2023 | 16 Feb 2028 |
最新表格
10.6- 2026.07
10.11 2028.02
来自官网 https://mariadb.org/about/#maintenance-policy
Currently maintained short-term releases
从上表我们可以清除看出 现在最佳版本是10.5 或者 10.6
不要安装10.7以后 因为支持时间短 兼容性一般 安装文件大 个人意见
接下来,大家可以参考下图记录MYSQL的各个版本的发布时间,来确认各个版本的最终补丁日期:
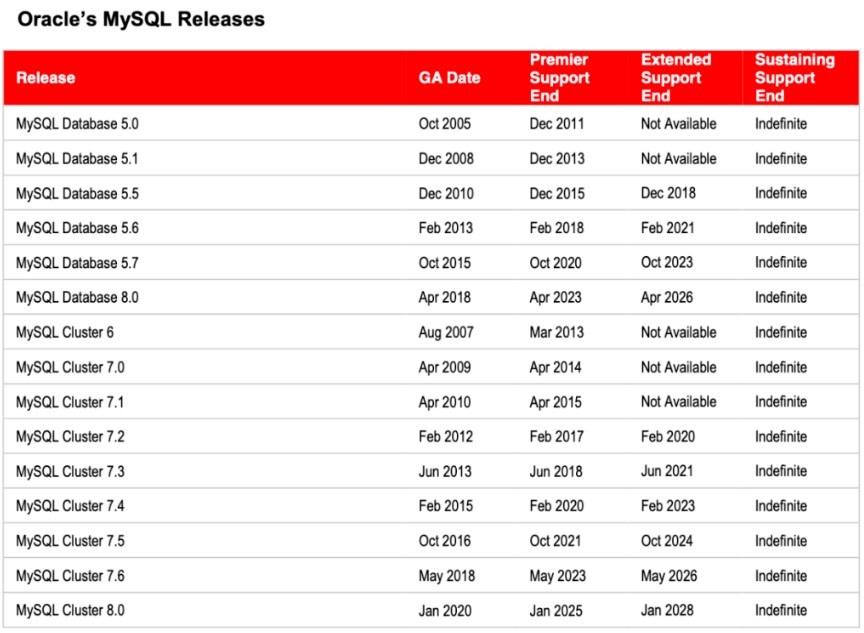
从上图可以看出,今年的10月份,5.7版本会停止标准支持阶段,进入延伸阶段,2023年10月以后,停止发布补丁。迫在眉睫的是5.6版本,明年2月以后,不会再提供任何补丁了,还在使用MySQL5.6版本的小伙伴,你的MySQL该升级了!
Additional milestones in MySQL development included:
First internal release on 23 May 1995
Version 3.19: End of 1996, from www.tcx.se
Version 3.20: January 1997
Windows version was released on 8 January 1998 for Windows 95 and NT
Version 3.21: production release 1998, from www.mysql.com
Version 3.22: alpha, beta from 1998
Version 3.23: beta from June 2000, production release 22 January 2001[24]
Version 4.0: beta from August 2002, production release March 2003 (unions).
Version 4.1: beta from June 2004, production release October 2004 (R-trees and B-trees, subqueries, prepared statements).
Version 5.0: beta from March 2005, production release October 2005 (cursors, stored procedures, triggers, views, XA transactions).
The developer of the Federated Storage Engine states that "The Federated Storage Engine is a proof-of-concept storage engine",[25] but the main distributions of MySQL version 5.0 included it and turned it on by default. Documentation of some of the short-comings appears in "MySQL Federated Tables: The Missing Manual".[26]
Sun Microsystems acquired MySQL AB in 2008.[27]
Version 5.1: production release 27 November 2008 (event scheduler, partitioning, plugin API, row-based replication, server log tables)
Version 5.1 contained 20 known crashing and wrong result bugs in addition to the 35 present in version 5.0 (almost all fixed as of release 5.1.51).[28]
MySQL 5.1 and 6.0-alpha showed poor performance when used for data warehousing – partly due to its inability to utilize multiple CPU cores for processing a single query.[29]
Oracle acquired Sun Microsystems on 27 January 2010.[30][31][32]
The day Oracle announced the purchase of Sun, Michael "Monty" Widenius forked MySQL, launching MariaDB, and took a swath of MySQL developers with him.[33]
Geir Høydalsvik, current Senior Software Development Director for MySQL at Oracle in 2018
MySQL Server 5.5 was generally available (as of December 2010). Enhancements and features include:
The default storage engine is InnoDB, which supports transactions and referential integrity constraints.
Improved InnoDB I/O subsystem[34]
Improved SMP support[35]
Semisynchronous replication.
SIGNAL and RESIGNAL statement in compliance with the SQL standard.
Support for supplementary Unicode character sets utf16, utf32, and utf8mb4.[a]
New options for user-defined partitioning.
MySQL Server 6.0.11-alpha was announced[36] on 22 May 2009 as the last release of the 6.0 line. Future MySQL Server development uses a New Release Model. Features developed for 6.0 are being incorporated into future releases.
The general availability of MySQL 5.6 was announced in February 2013.[37] New features included performance improvements to the query optimizer, higher transactional throughput in InnoDB, new NoSQL-style memcached APIs, improvements to partitioning for querying and managing very large tables, TIMESTAMP column type that correctly stores milliseconds, improvements to replication, and better performance monitoring by expanding the data available through the PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA.[38] The InnoDB storage engine also included support for full-text search and improved group commit performance.
The general availability of MySQL 5.7 was announced in October 2015.[39] As of MySQL 5.7.8, August 2015,[40] MySQL supports a native JSON data type defined by RFC 7159.[41]
MySQL Server 8.0 was announced in April 2018,[42] including NoSQL Document Store, atomic and crash safe DDL sentences and JSON Extended syntax, new functions, such as JSON table functions, improved sorting, and partial updates. Previous MySQL Server 8.0.0-dmr (Milestone Release) was announced 12 September 2016.[43]
MySQL was declared DBMS of the year 2019 from the DB-Engines ranking[44]
